|
1 General explanations and Credits 2 General terms 2.1 Two-dimensional shape 2.1.1 Outline 2.1.2 Apex 2.1.3 Base 2.1.4 Incision 2.1.5 Margin 2.2 Three-dimensional shape 2.2.1 Solidity + solid form 2.2.2 Cross section shape 2.3 Other 2.3.1 Position + surface shape |
3 Morphological terms 3.1 General 3.1.1 Surface structure 3.1.2 Texture + other 3.1.3 General elementes + armament 3.2 Indumentum 3.3 Growth form 3.3.1 General 3.3.2 Lifetime 3.3.3 Special 3.4 Subterranean and aerial parts 3.4.1 Subterranean parts 3.4.2 Aerial parts 3.6 Heads, receptacle + flower 3.7 Achene + pappus |
|
2. General terms |
|
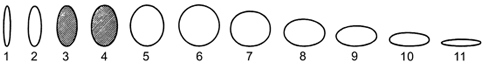
| elliptic | broadest at the middle with two equal rounded ends, the sides more gently rounded (1-5, 7-11) |
 |
|
|
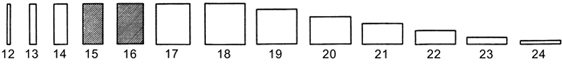
oblong |
longer than broad, with the margins parallel for most of their length (12-17, 19-24) |
|
linear |
narrow and much longer than wide, with parallel margins (12, 24) |
 |
|
|
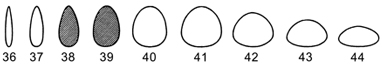
ovate |
egg-shaped, about twice as long as broad, with the wider part below the middle (36-44) |
|
lanceolate |
= narrowly ovate (36, 37) |
 |
|
|
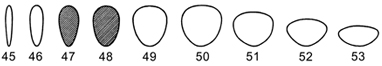
obovate |
egg-shaped with the broadest part near the apex (45-53) |
| spathulate | = oblanceolate = narrowly obovate (45, 46) |
 |
|
|
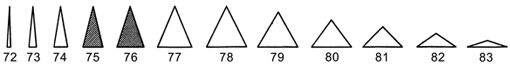
triangular |
having three angles, like a triangle (72-83) |
|
deltate |
shaped like a ± equal-sided triangle (78-79) |
 |
|
| acute | sharp, sharply pointed, the margins near the tip being almost straight and forming an angle of < 90°; opposite: obtuse |
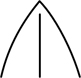 |
| acuminate | tapering to a long tip (usually of leaf tips)
|
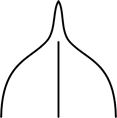 |
| mucronate | ending abruptly in short stiff point
|
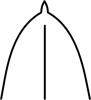 |
| obtuse | = blunt; not pointed; opposite: acute
|
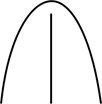 |
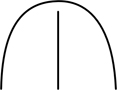
| rounded | smoothly curved, without abrupt angels
|
 |
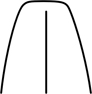
| truncate | ending abruptly in a more or less straight line, as if cut off
|
 |
| cuneate | tapering gradually, wedge-shaped | 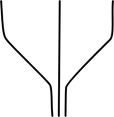 |
| truncate | ending abruptly in a more or less straight line, as if cut off | 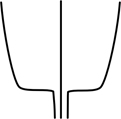 |
| attenuate | gradually tapering over a long distance | 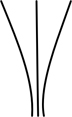 |
| cordate | deeply notched so the whole base has a slight heart-shape | 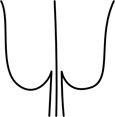 |
| hastate | with 2 ± triangular lobes diverging from the petiole apex | 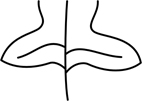 |
| sagittate | with 2 acute lobes, like an arrow-head | 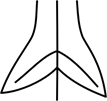 |
| oblique | when the two sides of the leaf are unequal near the base | 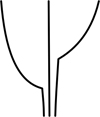 |
| peltate | round and attached in or near the centre; of a leaf, with the petiole attached to the blade, away from the margin | 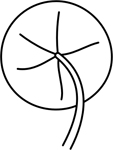 |
| auriculate | embracing/clasping the stem with ear-like structures | 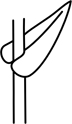 |
| clasping
|
= amplexicaul; embracing the stem, e.g. the leaf base extending to the side of the stem opposite to the main blade | |
| semi-amplexicaul | embracing half of the stem | |
| decurrent | extending downwards; said of leaf edges when they continue down the stem as wings or raised lines
|
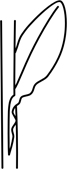 |
| entire | not divided | 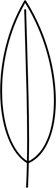 |
| pinnate | divided into a central axis and several lateral ribs or leaflets (like a feather) | |
| pinnatilobed | pinnately lobed = pinnately divided, depth of incision not specified |
|
| pinnatifid | pinnately divided clearly less than halfways, with shallow lobes |
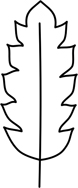 |
| runcinate | pinnatifid with the lobes pointing towards the base | 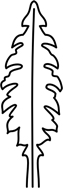 |
| pinnatipartite | pinnately divided to about halfway |  |
| pinnatisect | pinnately divided almost to midrib |  |
| lyrate | = lyriform; = lyre-shaped; pinnately divided with a large terminal lobe and being sinuate laterally | 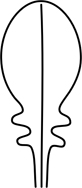 |
| lyrate-pinnatifid | = lyrately pinnatifid | |
| lyrate-pinnatisect | lyrately pinnatisect | |
| entire | smooth, unbroken by serrations, teeth or other irregularities | |
| dentate denticulate |
prominently toothed with acute symmetrical projections finely toothed |
|
| lacerate | torn at the margin, irregularly lobed, as if torn |  |
| laciniate | cut into slender lobes or drawn-out teeth |  |
| pectinate | like a comb, with very close narrow and parallel divisions | 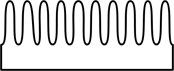 |
| serrate serrulate |
toothed like a saw, with regular acute and angled teeth minutely serrate |
|
| sinuate | when the margin is uneven, with rather deep rounded sinusoidal undulations | 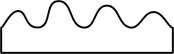 |
| spinose | with spines | 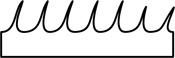 |
| undulate | wavy |  |
| ciliate | bearing a fringe of hairs along the margin | |
|
a. Solidity |
||
| hollow | unfilled; opposite: medullary | |
| medullary | pith-filled; opposite: hollow | |
|
b. Solid form |
||
| cylindrical | = cylindric; like a cylinder, i.e. long and narrow with a circular cross-section | |
| campanulate | bell-shaped; with a tube about as long as wide, and a flaring limb | 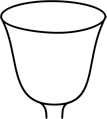 |
| clavate | = club-shaped; thickened towards the upper end | |
| ovoid | egg-shaped, with the broad part below the middle/nearest the base | 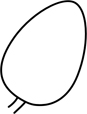 |
| obovoid | egg-shaped, with broadest part towards the apex | 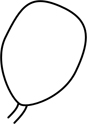 |
| fusiform | = spindle-shaped; thick, but tapering towards both ends | |
| turbinate | top-shaped, obconical and narrowed towards the point | 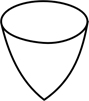 |
| hemispherical | = plano-convex; in the shape of half a sphere or globe | 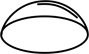 |
| funnel-shaped | = funnel-form = infundibuliform; proximally tubular, abruptly widening to a wider distal part | 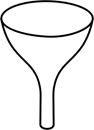 |
| terete | circular in cross-section, lacking grooves or ridges |  |
| angular | = angulate; with an edge, as where two planes meet | 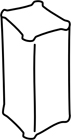 |
| triangular | with 3 edges | |
| ribbed | with longitudinal, distinctly convex elevations | |
| sulcate | grooved, furrowed with longitudinal grooves | |
| winged | with flattened to blade-like expansions | 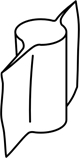 |
| canaliculated | = channelled; with a longitudinal channel or groove | |
|
a. Position |
||
| retrorse | = pointed downwards = recurved; bent abruptly backward or pointed towards the proximal part; opposite: antrorse |
 |
| antrorse | pointing towards the distal end, upwards or forwards; opposite: retrorse |  |
|
|
||
| spreading | = patent; held at 90° from the subtending axis | |
| spreading-erect | = erecto-patent; held at 45° from the subtending axis) | |
|
b. Surface shape |
||
| flat | having a horizontal surface | |
| convex | with a rounded surface, like the outside of a bowl; opposite: concave | 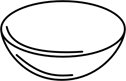 |
| concave | hollow, as the inside of a bowl; opposite: convex | |
| pitted | with small depressions (pits) | |
| alveolate | with pits looking like a honeycomb | 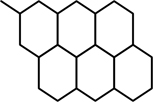 |
| foveolate | minutely pitted | |
| areolate | divided into distinct spaces by boundary lines | |
| smooth | even | |
| wrinkled | = rugose |  |
| muricate | rough, with short hard pointed protuberances |  |
| striate | with several fine, parallel, longitudinal grooves | 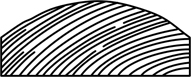 |
| tuberculate | covered with wart-like protuberances or knobs |  |
| verrucose | warty | |
|
a. Texture |
||
| leathery | = coriaceous; as tough as leather | |
| scarious | = membranaceous = membranous) thin and dry, not green | |
| cartilaginous | = cartilagineous = callose; hard and tough, but slightly bendy | |
| b. Other | ||
| homomorphic | units (e.g. achenes, pappus bristles) uniform (including minor gradual differences) | |
| heteromorphic | units not uniform, with structural differences | |
| dimorphic | two different types of units (e.g. outer and inner achenes of a head) | |
| uniseriate | in a single whorl or series | |
| biseriate | in two whorles or series | |
|
a. General elements |
|||
| trichome | an epidermal outgrowth | ||
| bristle | = seta; a stiff, rigid trichome | ||
| hair | an elongated single-celled or multi-celled trichome, without vascular tissue | ||
| papilla | trichome; a small elongated extension of one epidermal cell | ||
| scale | trichome; rather small, flat extension on the surfaces | ||
| prickle | a sharp outgrowth from the surface of a plant, involving several layers of cells but not containing a vein, detachable without tearing the organ | 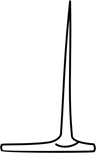 |
|
| spine | = thorn; a stiff, sharp-pointed structure, formed by modification of a plant organ, e.g. a lateral branch or a stipule, detachable only with tearing the organ | 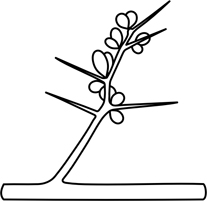 |
|
|
b) Armament (hairs) |
|||
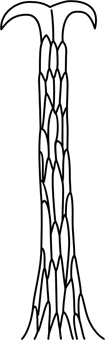
| forked hair |
(= bifid) divided at the tip in two (usually equal) parts by a median cleft | 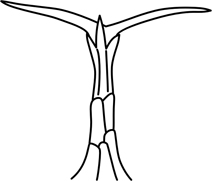 |
 |
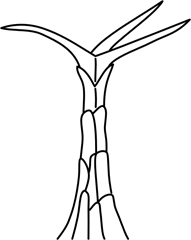
| stellate hair | star-shaped, with numerous arms radiating outwards | 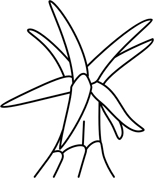 |
 |
| glabrous | without hairs, scales or other indumentums | |
| glabrescent | becoming glabrous or nearly so | |
| arachnoid | = cobwebbed; cobweb-like, tangled cottony, the hairs in several directions and tangling |  |
| cottony | with long, soft, weak, filamentous hairs, somewhat flocculent and entangled |  |
| floccose | bearing tufts of soft hairs or wool which tend to rub off and adhere in small masses | 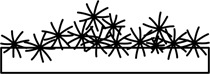 |
| hirsute | bearing coarse, stiff, long hairs |  |
| hispid
hispidulous |
= setose; with stiff hairs or bristles, rough to the touch
= strigillose; minutely hispid |
 |
| papillose | bearing papillae |  |
| pilose | hairy, the hairs soft and clearly separated but not sparse |  |
| pubescent | covered in fine, short, erect hairs |  |
| puberulous | = puberulent; shortly pubescent | |
| scabrid
|
= scabrous; rough to the touch, usually from the presence of minute stiff hairs |
 |
| scabridulous | minutely scabrid | |
| silky | = sericeous; with closely appressed, soft, straight, fine hairs and somewhat shiny |  |
| strigose | with sharp, stiff hairs appressed to the surface | |
| tomentose | densely covered in short soft hairs, these somewhat curly and matted |  |
| velvety | very densely covered with fine, short, soft, erect hairs |  |
| villose | = villous; shaggy, with long soft hairs | 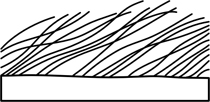 |
| woolly | = lanate = lanuginose; with tangled long hairs |  |
| glandular | covered with glands or with a zone of secretion-producing tissue | 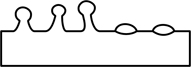 |
| viscid | sticky | |
| scaly | bearing scales | |
| tree | perennial woody plant with secondary thickening, with a clear main trunk. The distinction between tree and shrub is fluid, but generally accepted to be dependent on the single trunk, and on height, a tree being at least 2-3 m tall. | |
| shrub | self-supporting woody plant branching at or near the ground or with several stems from the base; also used for plants with a single stem but then ‘quite short’ (< 2 m) | |
| subshrub | shrub, with basally woody, apically herbaceous stems | |
| rosette shrub | branches all formed by the woody rosette axes, densely covered with the scars of the former rosette leaves, and with the leaves arranged in terminal rosettes | |
| dwarf shrub | shrub c. < 0.5 m tall | |
| herb | plant without persistent woody stem above ground | |
| rosette herb | herb with a permanent leaf rosette | |
| annual | completing its life cycle within one year or one growing season | |
| biennial | taking 2 years from seedling stage to maturity, seed-set and death, usually hibernating in the rosette stage | |
| pauciennial | living for a few years | |
| perennial | living for several to many years | |
| scapose | with a scape; said of herbs with a basal rosette and an head rising from the centre of the rosette on a leafless stalk | 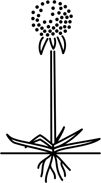 |
| acaulescent | = acaulous; without a stem (or without a visible stem) | |
| cushion-forming | many plants growing close together, forming a dense rounded mass | |
| rhizomatous | with an underground stem (rhizome) | |
| climbing | growing upwards by attaching itself to other structures which are used as supports | |
| scoparious | shaped like a broom, with several closely set, upward-pointing stems | |
| procumbent | trailing or spreading along the ground but not rooting at the nodes | 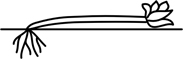 |
| ascending | growing erect after an oblique or semi-horizontal beginning | 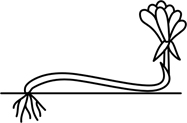 |
| rhizome | underground stem, as distinct from root; distinguished by its nodes, buds or scale-like leaves; growing either horizontally or oblique (ascending) | |
| taproot | the primary root, going straight down | |
| secondary root | a root branching from the primary root | |
| tuberous root | = tuber; a swollen root or branch of a root acting as a reserve store of nourishment or water | |
| root-born shoot | an elongated stem (shoot), which can arise from both the taproot and the lateral roots | |
| caudex | often woody, persisting shoot structure of perennial rosette plants. The rosette shoot terminates with a short-lived herbaceous flowering stem and axillary buds consecutively continue the growth of the primary rosette shoot. The result is a rosette axis, densely covered marchescent leaves or the scars of the former rosette leaves, which may become elongated, woody and branched, the plants becoming few-rosetted. | |
| flowering stem | the flowering stem is leafless or leafy, branched to certain extends or unbranched and its growth is terminated by the flower heads, which are disposed in varies ways, described as types of synflorescences. | |
| scape | the scape is an unbranched, essentially leafless and nodeless stalk of a single flower head, arising from a caudex or rhizome. | |
|
a. Position of heads |
||
| pendent | = pendant = pendulous = drooping; hanging or inclining downward | |
|
b. Receptacle |
||
| paleate | = paleaceous = scaly; with chaffy scales amongst the flowers | |
| epaleate | without scales | |
| bristly | with stiff strong hairs | |
| naked | lacking scales and bristles | |
|
c. Flowers shape |
||
| ligulate | corolla with a tubular base and a 5-toothed ligule | |
| tubular | cylindrical and hollow, with a 5-lobed limb | |
|
a. General |
||
| achenes | = cypsela; a small dry thin-walled fruit, not splitting when ripe, and containing a single seed | 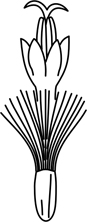 |
| pappus | a series of bristles, hairs or scales on the apex of the achene | |
|
b. Pappus persistence |
||
| persistent | remaining in place, not falling off; opposite: caducous | |
| caducous | falling off soon after formation; opposite: persistent | |
|
c. Pappus texture |
||
| fragile | easily broken or damaged | |
| flexible | = soft; capable of being bent, usually without breaking | |
|
d. Pappus type |
||
| paleaceous | = paleate; composed of scales, that are laterally fused hairs | |
| setaceous | bristle-like, narrow and stiff | |
|
e. Pappus bristle type |
||
| bristle | trichome-like pappus element composed of a certain smaller or larger number of cells in cross section shape usually attenuate distally | |
| fimbria | pl. fimbriae, side projection (= lateral projection) | |
| scabrid | = scabridulous; rough, with very short fimbriae | |
| denticulate | = toothed; with short teeth-like fimbriae | |
| barbellate | = long-toothed; with long teeth-like fimbriae, few times longer than diameter of the bristle | |
| plumose | with fimbriae many times longer than the diameter of the seta | |
| feather-like fimbriately plumose fimbriae arranged in one plane as is the case in a true feather |
||
| stiffly fimbriately plumose with stiff fimbriae pointing in all directions like a bottle-brush, each fimbria consisting of a single giant tubular cell resembling a macaroni |
||
| softly fimbriately plumose with soft and often interwined fimbriae pointing in all directions and consisting of a row of flattened cells resembling cotton fibers or knitting wool along the seta |
||